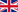
Howto use program: just enter the expression, the variables and their values, and finally, press ''=''.
In expression you can use the usual operators, such as ''+'', ''-'', ''*'', ''/'', and ''^'' - involution, ''%'' - modulo, ''!'' - factorial.
Also part of expression may be in parentheses to change priority operations.
In expression you may use constants:
$pi - number Pi (3.14159...)
$e - number e (2.71828...)
It is possible to save the function and used variables for subsequent calculations.
When you enter numbers, you can use the E notation, for example, 1.3e5 i.e. 130000.
Value of the trigonometric functions depends on the position of the switch:
DEG - degrees
RAD - radians
GRAD - gradians
List of supported functions
Trigonometric functions
sin(x) - sine of x
cos(x) - cosine of x
tg(x) - tangent of x
tan(x) - also tangent of x
ctg(x) - cotanget of x
cot(x) - also cotanget of x
sec(x) - secant of x
cosec(x) - cosecant of x
csc(x) - also cosecant of x
arcsin(x) - arcsine of x
arccos(x) - arccosine of x
arctg(x) - arctangent of x
arctan(x) - also arctangent of x
arcctg(x) - arccotangent of x
arccot(x) - also arccotangent of x
arcsec(x) - arcsecant of x
arccosec(x) - arccosecant of x
arccsc(x) - also arccosecant of x
Hyperbolic function
sinh(x) - hiperbolic sine of x
sh(x) - also hiperbolic sine of x
cosh(x) - hiperbolic cosine of x
ch(x) - also hiperbolic cosine of x
tanh(x) - hiperbolic tangents of x
th(x) - also hiperbolic tangents of x
coth(x) - hiperbolic cotangent of x
cth(x) - also hiperbolic cotangent of x
sech(x) - hiperbolic secant of x
cosech(x) - hiperbolic cosecant of x
csch(x) - also hiperbolic cosecant of x
arsh(x) - inverse hiperbolic sine of x
arch(x) - inverse hiperbolic cosine of x
arth(x) - inverse hiperbolic tangent of x
arcth(x) - inverse hiperbolic cotangent of x
arsch1(x) - inverse hiperbolic secant of x (with plus sign)
arsch2(x) - inverse hiperbolic secant of x (with minus sign)
arcsch(x) - inverse hiperbolic cosecant of x
Other functions
abs(x) - absolute value of x
lg(x) - common logarithm of x
log10(x) - also common logarithm of x
ln(x) - natural logarithm of x
log2(x) - binary logarithm of x
log(b, x) - logarithm of x to base b
exp(x) - exponential function of x
sqrt(x) - square root of x
cbrt(x) - cube root of x
round(x) - rounded value of x
rand(x) - random value from 0 to x
pow(x, y) - x raised to power y, y maybe less then 1, for example, pow(8, 1/3) - cube root of 8